This video was published on 2019-10-12 19:47:29 GMT by @Anatomy-Knowledge on Youtube.
Anatomy Knowledge has total 146K subscribers on
Youtube and has a total of 119 video.This video has received 1.2K
Likes which are higher than the average likes that Anatomy Knowledge gets . @Anatomy-Knowledge receives an average views of 14.3K
per video on Youtube.This video has received 44
comments which are higher than the average comments that Anatomy Knowledge gets .
Overall the views for this video was lower than the average for the profile.Anatomy Knowledge #cubitalfossa #brachial #mediannerve has been used frequently in this Post.









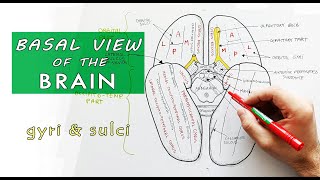


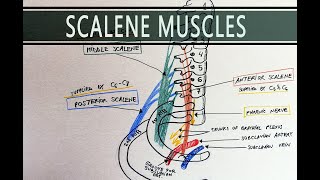





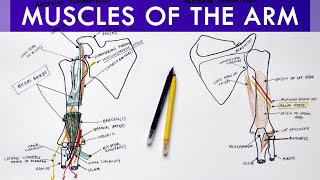
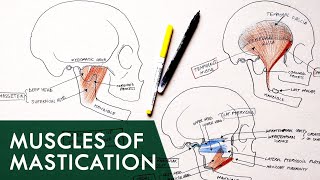
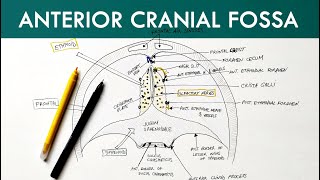



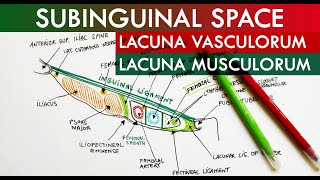


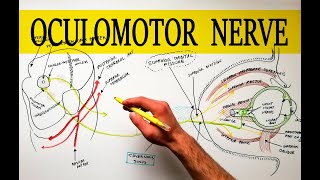
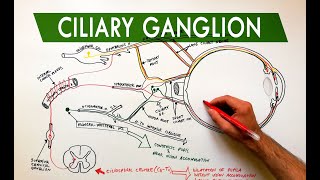

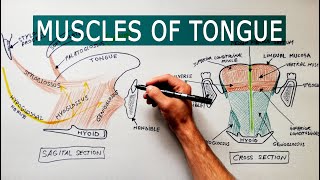

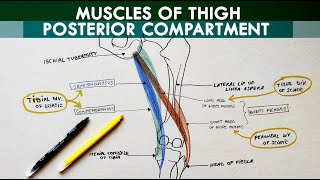
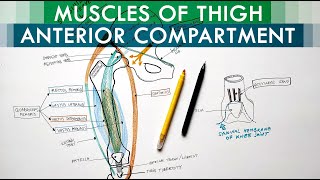


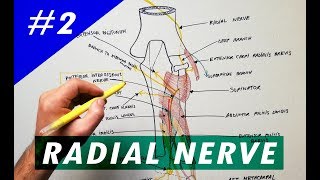












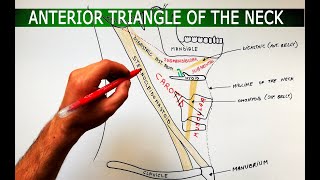





Anatomy Knowledge's video: Cubital Fossa Borders Contents Anatomy Tutorial
1.2K
44