This video was published on 2024-05-22 21:00:01 GMT by @Solution--Pharmacy on Youtube.
Solution- Pharmacy has total 0.9M subscribers on
Youtube and has a total of 2.5K video.This video has received 11
Likes which are lower than the average likes that Solution- Pharmacy gets . @Solution--Pharmacy receives an average views of 2.2K
per video on Youtube.This video has received 2
comments which are lower than the average comments that Solution- Pharmacy gets .
Overall the views for this video was lower than the average for the profile.Solution- Pharmacy #solutionpharmacy #Pharmacologyclass #Pharmacognosyvideos #GPAT has been used frequently in this Post.
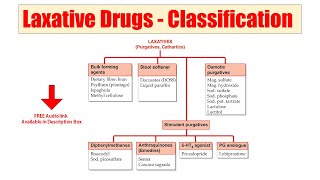


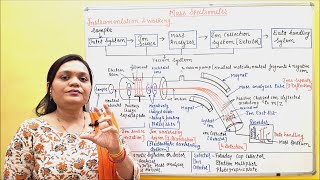



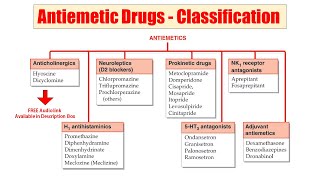















































Solution- Pharmacy's video: Spectroscopy Part 8 Mass Spectroscopy Part 2 Instrumentation Working Phytochemistry Part 38
11
2